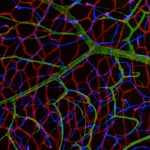
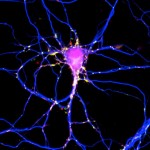
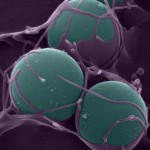
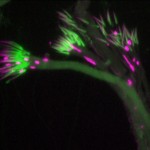
The power of the Image. As author and cartoonist James Thurber once observed “There are two kinds of light – the glow that illuminates, and the glare that obscures”. Cell biology would be nowhere without some photons to drench the otherwise dim and often lifeless specimens that we so carefully produce. Thanks to some remarkable developments in microscopes and staining tools, we can easily capture images and sit in awe and wonder at the hitherto invisible beauty found in nature. So what makes an image an outstanding image? Is it the biology underlying? Is it the technical prowess of the sample maker? Is it the composition or colour choice? Is it all these together? It is probably all or at least most of the above.
The rules and regulations for the image competition can be found here.
The competition entry deadline is usually in February or Marcj and will be posted in our news section on the homepage of the website and communicated to members by email.
The deadline for entries this year (2024) is March 31st. Prize winners will be announced at the joint BSCB/Biochemical Society Cell Migration meeting in April 2024.
The 2023 Image prize winners can be viewed here.
Previous Competitions
BSCB Competition Winners 2022
-
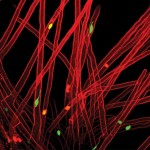
3rd prize: Tom Mitchell
Proximity labelling is a powerful tool to investigate protein trafficking. In these HUVECs a fusion protein of neuropilin-1 and HRP biotinylated proteins within a 20 nm radius (streptavidin, gold). This reveals a highly striated pattern of bounded by, and overlapping the cell junctions (PECAM-1, blue). Nuclei visualised via DAPI (Purple).
-
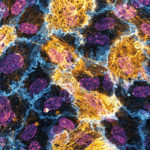
2nd prize: Sam Dunkley
Single slice Airyscan image of a C57Bl/6 mouse oocyte arrested at metaphase-I of Meiosis. Actin filaments can be seen permeating the microtubule-based spindle. Chromosome labelled with Hoechst (blue), the microtubule spindle by tubulin (green) and actin with phalloidin (magenta). The image was taken using a Zeiss LSM 800 with Airyscan.
-
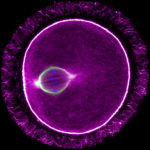
1st prize: Felix Mikus
Time series projection of the slime mould Physarum polycephalum (a.k.a. The Blob) colonising an agar plate. Actomyosin contractions allow this single, giant cell - containing thousands of nuclei sharing a single cytoplasm - to “expand” at centimetres per hour, making it large enough to be photographed using an iPhone 11.
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2021
-
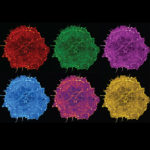
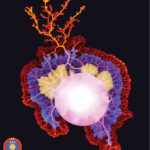
3rd prize: Hoang Anh Le
Drops of colour. This is a still image from a live imaging movie of a COS-7 cell expressing the marker LifeAct showing the intricate network of the actin cytoskeleton. The image is inspired by the Pop Art style picture of Marilyn Monroe by Andy Warhol.
-
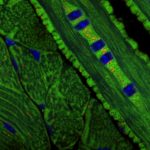
2nd prize: Alan Prescott
Mitochondrial organisation and turnover in the tongue revealed by the mitoQC mouse model Images taken from a frozen section of the tongue from the mitoQC mouse. Mitochondria are labelled with GFP(Green) and mCherry(Red). Nuclei are blue.
-
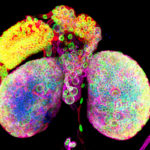
1st prize: Chantal Roubinet
Psychedelic brain: these beautiful brain lobes from Drosophila larvae illustrate the diversity of the cells that work together to generate a functional brain. This confocal image shows the nuclear envelope of nuclei in green (Lamin), the chromatin in blue (DAPI), Tubulin in Magenta and a cortical marker in red (dMoesin)
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2020
-
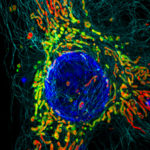
1st Prize: Hope Isobel Needs
Structured Illumination Microscopy (SIM) image of a HeLa cell expressing mScarlet localised to the mitochondrial matrix (red). Mitochondrial membranes are shown in green (MitoTracker Green), cell nuclei are labelled with DAPI (blue), and tubulin is shown in cyan. The image was taken using a DeltaVision OMX v4 imaging system (GE Healthcare).
-
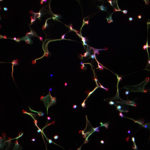
3rd Prize: Drinalda Cela
This fluorescence microscopy image shows neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), produced in response to haem and TNF stimulation. NETs are composed of DNA (in blue), granule proteins (such as neutrophil elastase, in red) and histones (in green). When neutrophils die via NETosis they release these web-like structures, which trap microbes and stimulate additional immune responses.
-
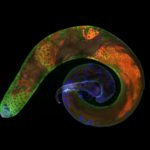
2nd Prize: Karl Norris
Spermatogenesis in a Drosophila melanogaster testis: in contact with hub cells (testis tip, violet: Armadillo), the somatic and germline stem cells give rise to gonialblasts that undergo mitosis (green: Vasa), meiosis and spermiogenesis. The latter two stages are stained in red (Fmr1), nuclei are stained by DAPI (blue).
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2019
-
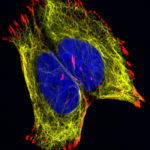
2nd Prize: Lisa Romano
The confocal image shows neuroblastoma cells cultured in a fibronectin coated coverslip, which allowed the formation of focal adhesion structure required during cell migration. The labelling is for vimentin in yellow (cytoskeleton), red for focal adhesion marker vinculin and blue staining for nuclei (DAPI).
-
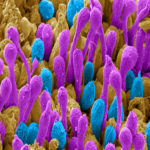
1st Prize: Patrick Ovando Roche
Scanning electron microscopy image of a 16-week-old human retinal organoid generated from pluripotent stem cells using bioreactor technology. Image has been pseudo-coloured to highlight rod (Purple) and cone (Cyan) photoreceptor outer-segments, the cell structures of the retina capable of capturing light and transforming it into vision.
-
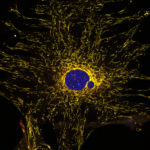
3rd Prize: Alan Prescott
Confocal image of a cultured mouse embryo fibroblast from the mito-QC mouse. Mitochondria express both eGFP and mCherry but in lysosomes the eGFP, green fluorescence is quenched. Bright red dots are mitolysosomes. The nucleus is DAPI stained, blue.
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2018
-
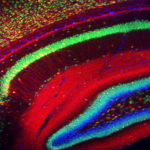
2nd Prize: Alessandro Bossio
Rainbow in the mouse hippocampus: the hippocampus is a region of the brain important for learning and memory. In this single stack confocal image nuclei are labelled in blue, mature neurons in green, axons and dendrites from cells infected by AAV1 virus to express mCherry are visible in red.
-
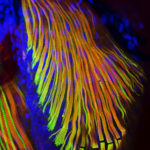
1st Prize: Massimo Ganassi
The beautiful microscopic structure of pectoral fin and hypaxial muscles of a Danio rerio larvae is revealed by immunostaining of fast (red) and slow (green) myosins. All nuclei are highlighted in blue.
-
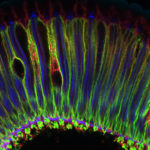
3rd Prize: Sonia Muliyil
Waves in the retina (Snapshot of a Drosophila adult retina) : This confocal image shows a tangential section of the Drosophila adult retina comprised of multiple photoreceptors and inter-ommatidial cells. Phalloidin (blue) marks the photoreceptor light sensitive membranes, also known as the rhabdomeres ,present apically while Na+ -K+ ATPase (green) marks the baso-lateral membranes of the Photoreceptors. This section is also co-labeled with an anti-caspase antibody (red).
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2017
-
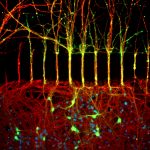
1st Prize: Cristiano Lucci
The image shows primary cortical neurons cultured in these compartmentalised microfluidic chambers. The labelling is for acetylated tubulin in red (identifying all axons), and green for the cell permeable dye calcein, which is only applied on the axonal side of the chambers (top half) and allows the identification of those neuronal cell bodies (bottom half) that have extended axons to the other side of the microfluidic device. Blue staining indicates nuclei labelled with DAPI. The image was taken using a fluorescent microscope at the SLIM facility in the School of Life Sciences.
-
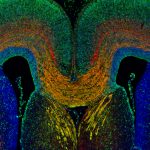
2nd Prize; Anneliese Norris
A section through the embryonic mouse telencephalon at E18.5 showing the L1 expressing corpus callosum (labelled orange) and cells of cortical origin labelled with GFP (green). Section is counterstain with DAPI (blue).
-
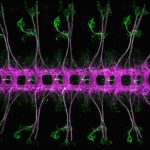
3rd = Mohammad Moffateh
Beautifully repeated segments of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic nervous system, stage 16/17, ventral view. Stained for Futsch (green, segmented sensory neurons and dispersed cell bodies in the ventral nerve cord) and Ank2-L (magenta, segmented ventral nerve cord and a subset of sensory neurons). Imaged with a Zeiss LSM780 confocal microscope.
-
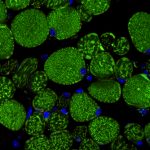
3rd = Alan Prescott
Confocal image of a transverse section of the rectus muscle of the eye taken from the mito-QC mouse (McWilliams et al., (2016) JCB, 214(3)). Mitochondria express eGFP and mCherry but in lysosomes the eGFP, green fluorescence is quenched. Bright red dots are mitolysosomes. Nuclei are DAPI blue.
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2016
-
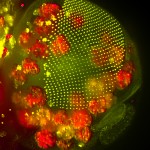
1st Prize: Anna Franz
The head of a Drosophila pupa: The developing compound eye (green) is composed of several hundred simple units called ommatidia arranged in an extremely regular array. The giant polyploidy cells of the fat body (red), the fly equivalent of the mammalian liver and adipose tissue, occupy a big area of the head.
-
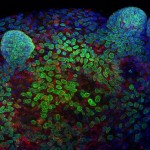
2nd Prize: Ronan Mellin
Confocal image showing a murine colonic epithelial organoid grown in Matrigel (3D culture). Crypt-like projections containing epithelial progenitors can be seen protruding from the spheroid. Stained for DNA with DAPI (Blue), the nuclear envelope with LaminB1 (Green) and the centrosome marker γ-tubulin (Red).
-
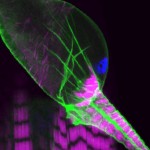
3rd Prize: Helen Weavers
This confocal image shows the intricate structure of the developing fly kidney, which is anchored within the body by attachment to nearby heart muscle. The striking striations of the heart (and body wall muscle beneath) are revealed by labeling Actin (majenta). Cell membranes (green) and nuclei (blue) are also stained.
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2015
-
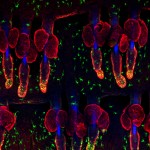
1st Prize: Kif Liakath-Ali
Exquisitely dotted melanocytes of mouse skin revealed by anti-TRP1 staining (Green) and individual hair follicles stained by anti-keratin14 (Red). Blue indicates DAPI staining of cell nuclei and autofluorescent hair shafts. Wholemount immunostaining was carried out on mouse tail epidermis.
-
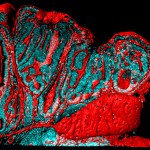
2nd Prize: Alistair Langlands
Small intestinal polyp of an ApcMin mouse. An IMARIS-rendered surface of Phalloidin (red) and nuclei (cyan) show changes associated with early cancer development. Normal structure is lost as the lumen becomes highly folded and epithelial cells start piling on top of one another due to excess proliferation.
-
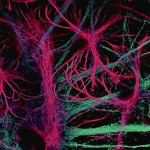
3rd Prize: Joanna Wardyn
This is a confocal image showing intricate structure of astroglial cells (pink, stained with anti GFAP antibody) interconnected with neurons (stained light blue with anti-β III tubulin). Astrocytes are increasingly appreciated as key modulators of neuronal health and function.
You can find out more about the people behind the images here
BSCB Competition Winners 2014
-
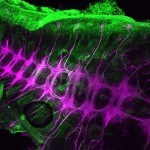
First Prize: Dr. Anna Franz, School of Biochemistry, Faculty of Medical Sciences, University of Bristol.
The beauty and complexity of the central nervous system of a grasshopper embryo is revealed by anti-HRP staining (coloured purple). Other tissues are stained with anti-acetylated tubulin (coloured green).
-
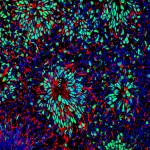
Dr. Patrick Ovando-Roche, Institute of Reproductive and Developmental Biology, Faculty of Medicine, Imperial College London
Neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells (hESCs): Following neural induction of hESCs, cells form neural rosettes structures to give rise to neural progenitors. Neural rosettes can be spotted by their rosette-like conformation and positive co-expression of pax6 (green) and nestin (red). Cell nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue).
-
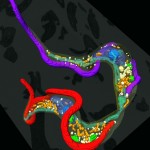
Dr. Louise Hughes, Bio-Imaging Unit, Department of Biological and Medical Sciences, Oxford Brookes University, Oxford.
Kissing trypanosomes: The image shows the final stage of cell division for the single-celled parasite, Trypanosoma brucei, with the two daughter cells connected at their posterior end. The image is generated from reconstructed data from serial block face scanning electron microscopy, showing the cells, their flagella (red and purple) and internal organelles.
-
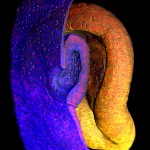
Highly commended: Timothy Grocott, School of Biological Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich.
Multi-photon imaging of the embryonic eye: A false-coloured image showing a cutaway through the invaginating lens placode (blue tissue layer) situated within the optic cup (yellow tissue layer) of a 2.5-day chick embryo. The surrounding mesenchyme was removed for clarity, while cell nuclei are labelled red.
-
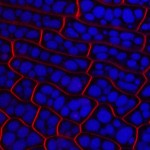
Highly Commended: Dr. Mistianne Feeney, School of Life Sciences, University of Warwick, Coventry
Arabidopsis thaliana embryo cells imaged by confocal microscopy. Long Caption: The plasma membrane of the Arabidopsis thaliana embryo cells is stained with FM4-64 (shown in red) and protein storage vacuoles autofluoresce (shown in blue).
You can find out more about the people behind the images here.
BSCB Competition Winners 2012
-
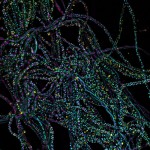
First Prize: Sheng-Wen Chiu, Department of Biochemistry, University of Oxford
In filamentous cells of the bacterium Rhodobacter sphaeroides, the tubulin homolog FtsZ (tagged with CFP) forms dot-like and spiral structures in two distinct populations. The FtsZ cytoskeleton affects the localization of the membrane chemosensory protein clusters (YFP). Cell bodies are shown in magenta.
-
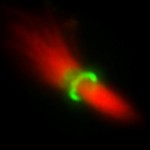
Second Prize: Zuni Irma Bassi, Department of Pathology, University of Cambridge
The image shows a midbody purified from HeLa cells synchronized in cytokinesis that has been fixed and immuno-stained to detect tubulin (shown in red) and Citron kinase (shown in green).
-

Third Prize: Dr Daniel Booth, Wellcome Trust Centre for Cell Biology, University of Edinburgh
A scanning electron micrograph (SEM) of DT-40 cells adhered to glass and fixed with aldehydes. The cells were pseudo coloured to make them resemble scoops of ice-cream.
BSCB Competition Winners 2011
BSCB Competition Winners 2010
Click an image to open gallery. |
The rules and regulations for the image competition can be found here.